What is orientation in math?
Orientation is one of the important terms and concepts that we are learning in the geometry of mathematics.
What is orientation in math?
The most basic definition of orientation is “the direction the object is facing” or “the way the object is facing”.
What is the meaning of the same orientation?
The same orientation in Math denotes that the points of objects are facing exactly the same directions as the original object.
Example:
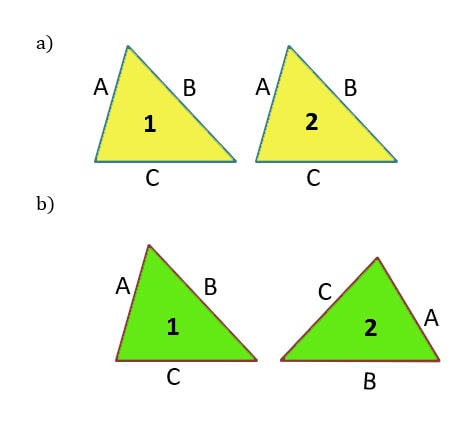
Determine whether two triangles have the same orientation.
Check Our What does bounded mean in math?
Solution:
a) 2 triangles have the same orientation.
Both triangles have base C at the bottom. The first triangle’s leg A is parallel to the second triangle’s leg A. The first triangle’s leg B is parallel to the second triangle’s leg B. As a result, we can determine that both triangles have the same orientation.
b) 2 triangles do not have the same orientation.
C is the base of the first triangle. The base of the second triangle, on the other hand, is B. Leg A of the first triangle is on the left, and Leg A of the second triangle is on the right. As a result, we can see that the two triangles do not have the same orientation.
The positioning of points in relation to one another following a transformation or rotation of a geometric figure is the actual definition of orientation in Math. Orientation is divided into two sections based on how the points align.
Check Our What does a comma mean in math?
Do all transformations alter an object’s orientation?
Some transformations do not affect an object’s orientation, while others affect it. We’ll go into more detail about this.
What is transformation in math?
Operations that change the form of a figure are called transformations. Reflections, translations, rotations, and dilations are the most common transformations.
In the following step, we’ll examine which transformations would cause a shape’s math orientation to change and which transformations would not.
Which transformations alter the orientation of an object?
Reflection
A reflection is a transformation in which a figure is flipped across a line. The reflection does not affect the original figure’s size or shape.
Example:
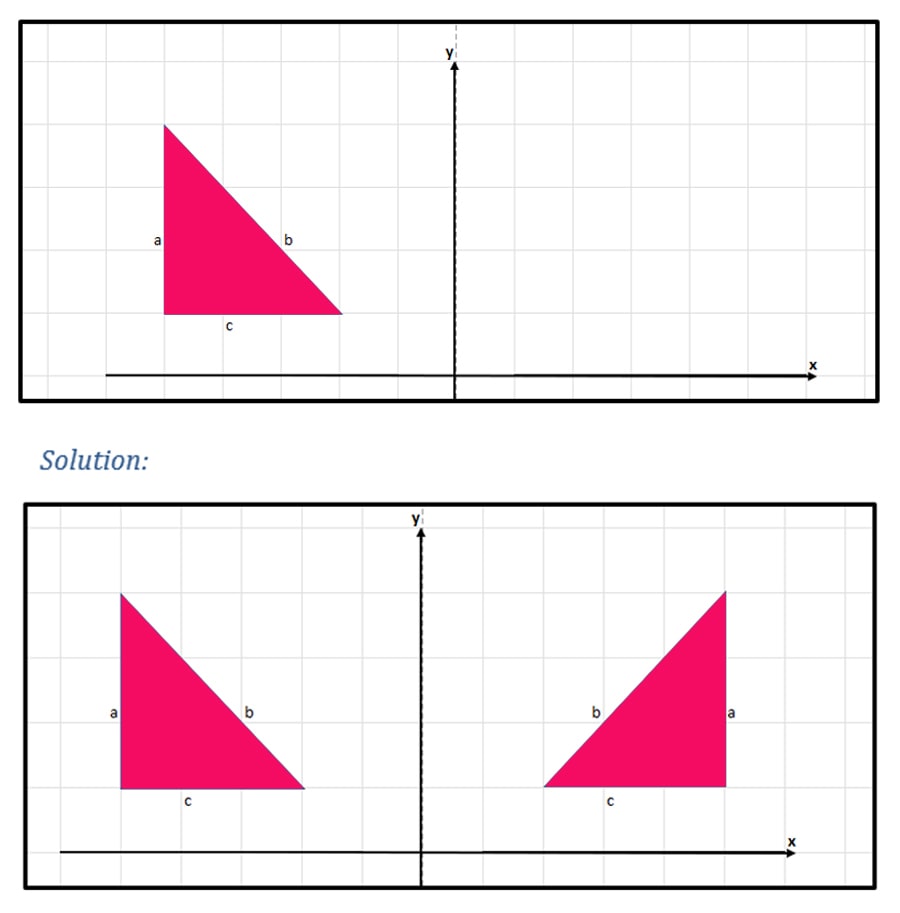
Make a reflection of the given triangle and comment on its orientation.
Check Our What does exp mean in math?
Even though the bases of both triangles are facing the same direction, the other 2 legs of the triangles are facing the complete opposite. We can identify that the 2 triangles do not have the same orientation.
Therefore, reflection does not preserve the orientation of an original shape.
Rotation
Rotation is the process of rotating a figure around a point by a specific degree. The rotation does not affect the original figure’s size or shape.
Example:
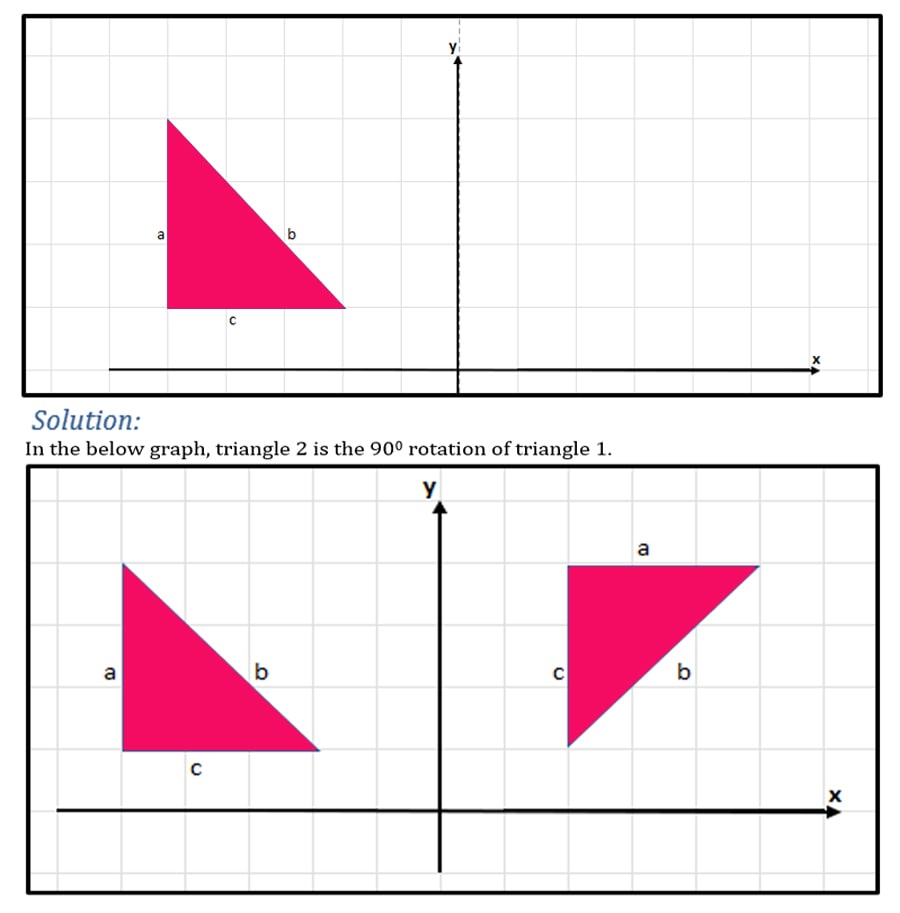
Rotate the given triangle by 900 and comment on its orientation.
Check Our What does half mean in math?
Observing the above 2 triangles, we can identify that the 2 triangles do not have the same orientation if we rotate the object 90 degrees.
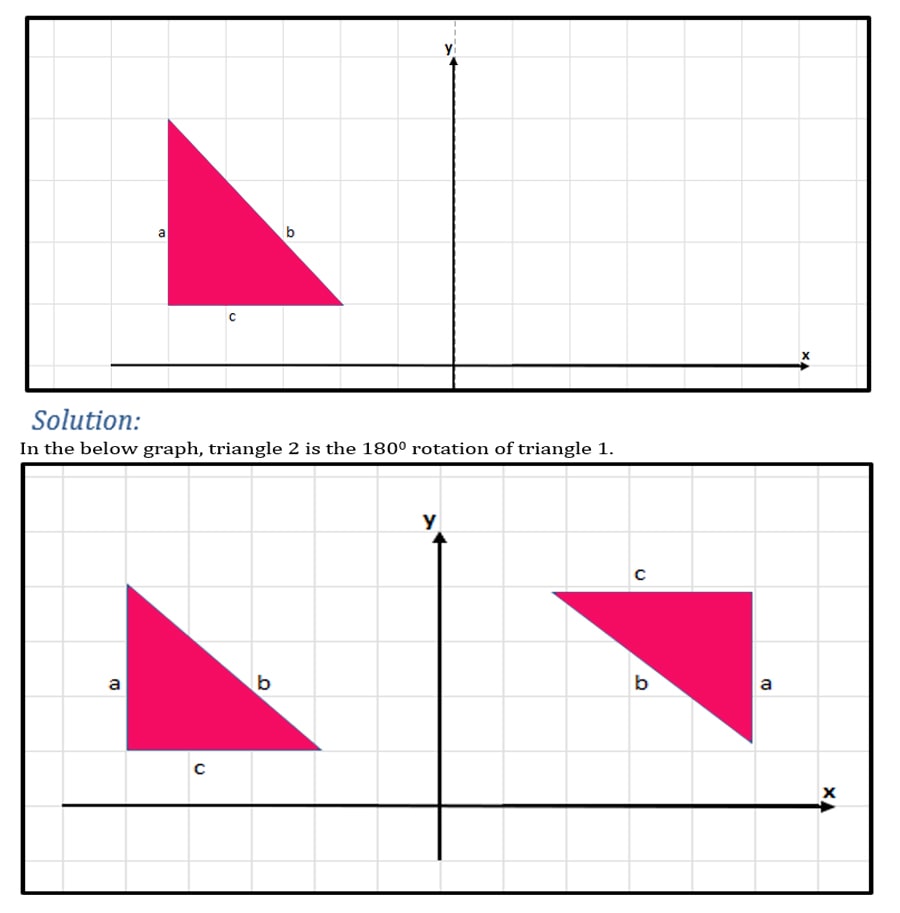
Example:
Rotate the given triangle by 180 and comment on its orientation.
Check Our What does lb mean in math?
Observing the above 2 triangles, we can identify that the 2 triangles do not have the same orientation if we rotate the object 180 degrees.
Generally, rotation does not preserve the orientation of the original shape. There is an exception for this. We will discuss this in the next section.
Which transformations do not alter the orientation of an object?
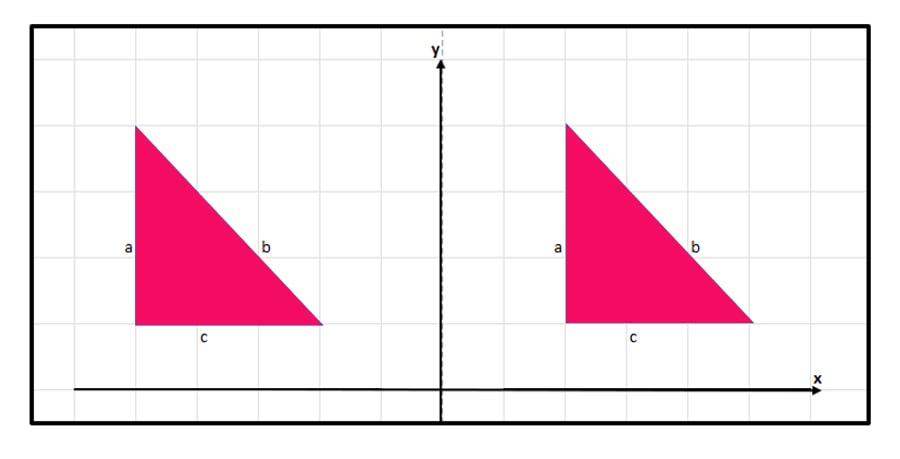
Rotation of 360 degrees
If we rotate an object 360 degrees, the rotated object’s alignment is exactly equal to the original object. Hence, orientation is the same as the original object.
Check Our What does the letter p mean in math?
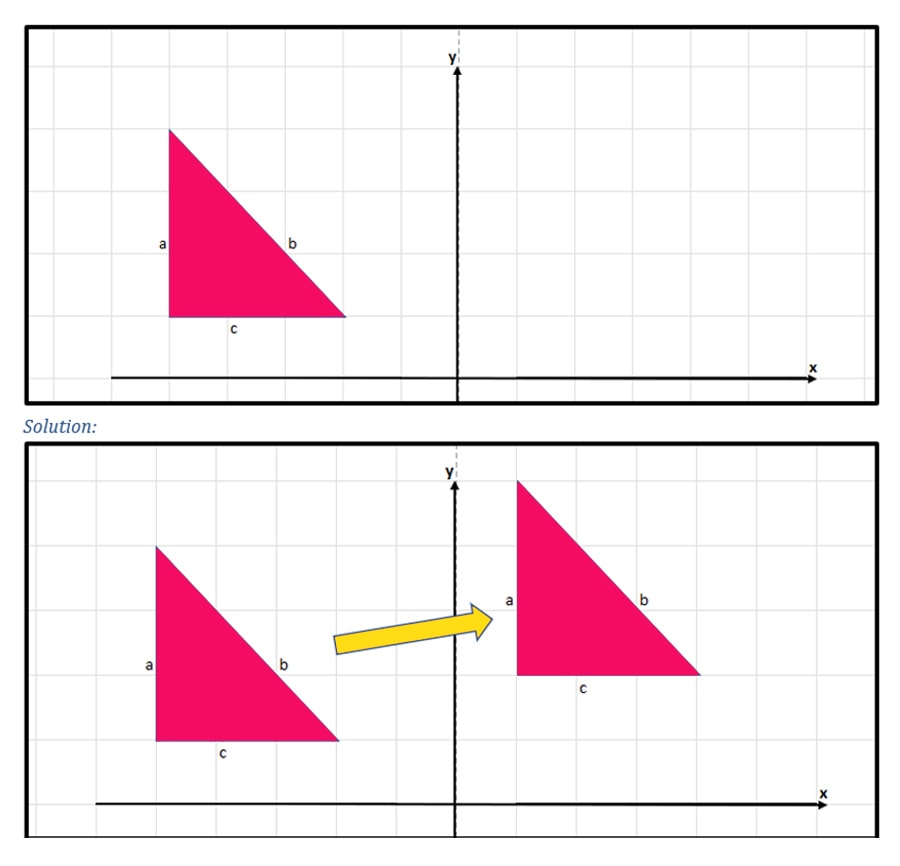
Translation
Moving an object in any direction without rotating while keeping the original size and shape is called translation.
Example:
Slide the given triangle in any direction without rotating and comment on its orientation.
Check Our What does no more mean in math?
Base C is located at the base of both triangles. The first triangle’s leg A is parallel to the second triangle’s leg A. The first triangle’s leg B is parallel to the second triangle’s leg B. We can see that both triangles are oriented the same way.
Therefore, translation preserves the orientation of the original shape.
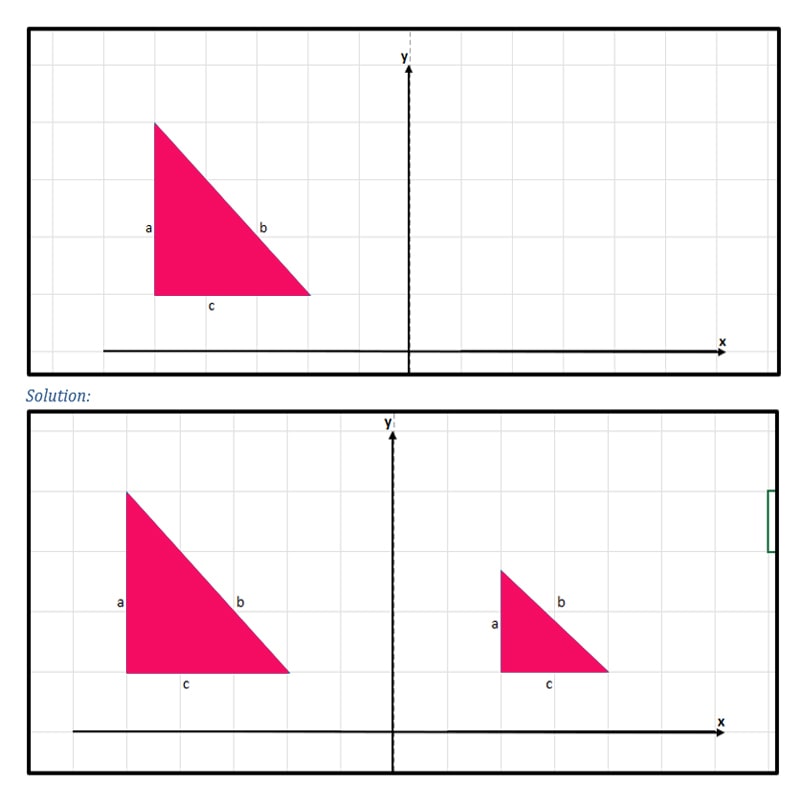
Dilation
Enlarging or reducing the size of an object without changing the shape and without rotating is called dilation.
Example:
Reduce the size of the given triangle and comment on its orientation.
Check Our What does o mean in math?
Both triangles have base C at the bottom. The 1st triangle’s leg A is parallel to the 2nd triangle’s leg A. The 1st triangle’s leg B is parallel to the 2nd triangle’s leg B. Both triangles have the same orientation, as we can see.
Therefore, dilation preserves the orientation of an original shape.
Frequently Asked Questions
The orientation is “the direction the object is facing” or “the way the object is facing”.
Reflection
Rotation except for 360 degrees
No. When we rotate an object 360 degrees, the alignment of the rotated object is exactly the same as the alignment of the original object. As a result, the orientation is the same as the original object.
Rotation of 360 degrees
Translation
Dilation